注:
非静态内部类和外部类有同名变量和方法时,需要通过Outer.this方式来访问外部类成员变量或方法。
成员内部类
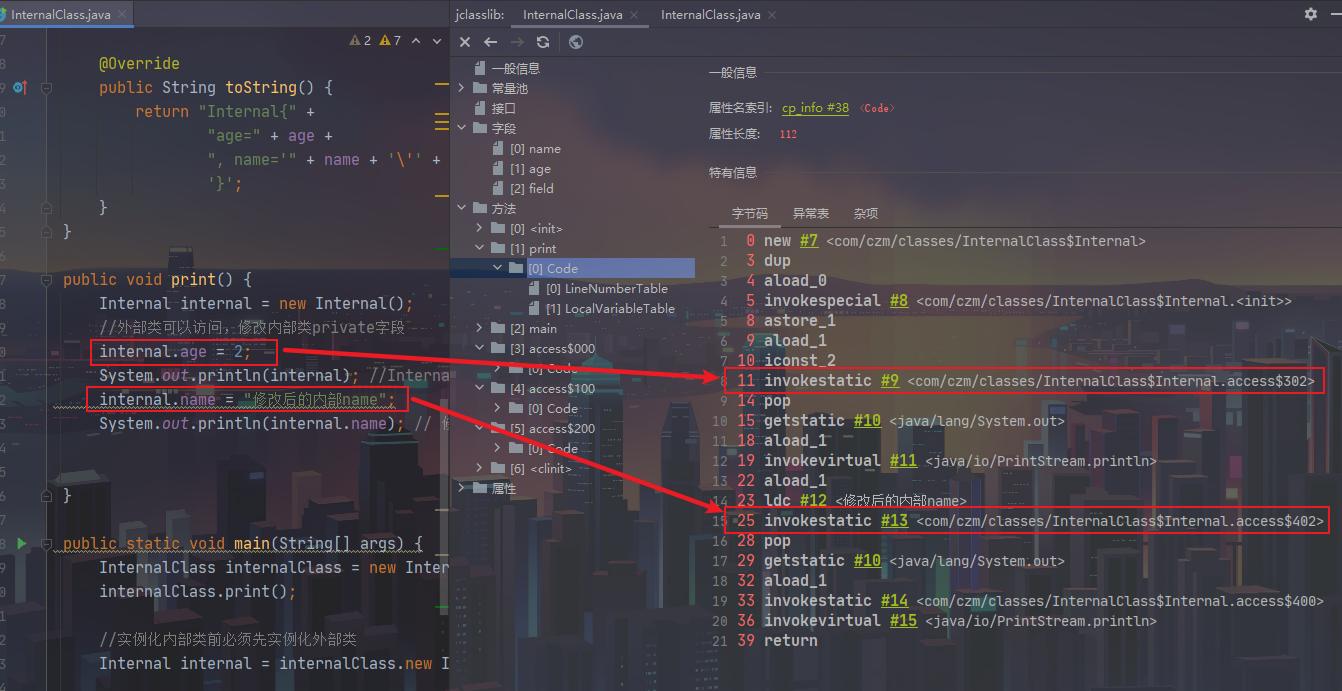
定义在一个类的内部,外部类的每个对象都会加载一次,不可以定义静态成员和方法,可访问外部类的所有私有字段/方法,
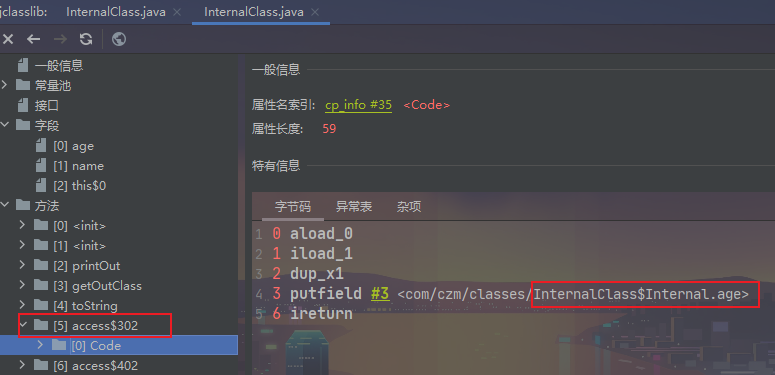
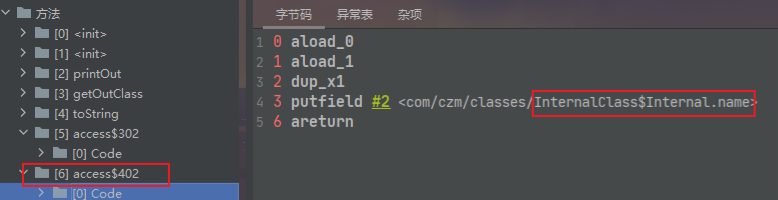
对于私有字段,访问,编译器会生成一个access函数提供调用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
|
public class InternalClass {
private String name = "默认名";
private static int age = 9;
private float field = 2.1f;
public class Internal {
private int age;
private String name = "内部类的默认name";
public Internal() {
}
public Internal(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void printOut() {
System.out.println(field);
System.out.println("内部age:" + age);
System.out.println("内部name:" + name);
System.out.println("外部age:" + InternalClass.age);
System.out.println("外部name:" + InternalClass.this.name);
}
private InternalClass getOutClass() {
return InternalClass.this;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Internal{" +
"age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
public void print() {
Internal internal = new Internal();
internal.age = 2;
System.out.println(internal);
internal.name = "修改后的内部name";
System.out.println(internal.name);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
InternalClass internalClass = new InternalClass();
internalClass.print();
Internal internal = internalClass.new Internal();
internal.printOut();
System.out.println(internalClass == internal.getOutClass());
Class1 class1 = new Class1();
System.out.println(class1.age1);
}
}
|
局部内部类
定义载方法内部或作用域内,不能被public、private、static修饰。可以直接访问外部类的成员。外部类无法直接创建局部内部类的实例,局部内部类可直接使用成员内部类。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
|
public class MethodClass {
private int outNUm = 1;
private int num2 = 2;
class InClass {
}
public void test1(){
int test1Field = 111;
class Method{
private int num1 = outNUm * 4;
private int num2 = 5;
InClass inClass = new InClass();
public void method1() {
System.out.println("局部内部类访问本地方法的变量:"+test1Field);
}
}
Method method = new Method();
System.out.println(method.num1);
System.out.println("外部num2"+MethodClass.this.num2);
System.out.println(method.num2);
method.method1();
}
private void test2(){
if(true){
class Partial{
private String id;
private String getId(){
return id;
}
}
Partial ts = new Partial();
ts.id = "123";
System.out.println(ts.getId());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MethodClass methodClass = new MethodClass();
methodClass.test1();
methodClass.test2();
}
}
|
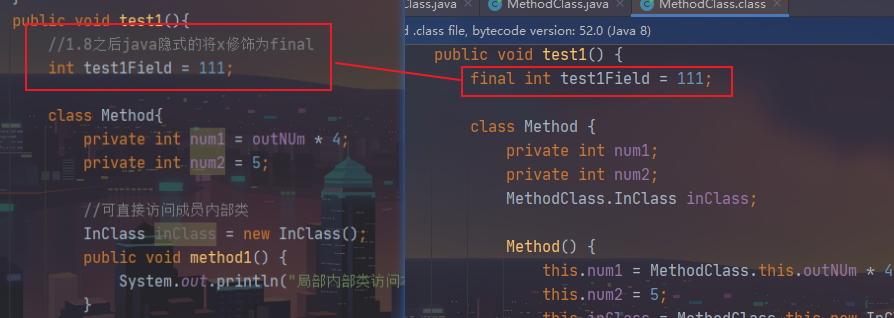
局部内部类访问局部变量,局部变量必须加final修饰。
因为局部变量会随着方法的调用完毕而消失,这个时候,局部对象并没有立马从堆内存中消失,局部对象还要使用这个局部变量。为了让数据还能继续被使用,就用fian1修饰局部变量,这样,在堆内存里面存储的其实是一个常量值。
匿名内部类
一个接口的实现类,或者是继承于某个父类的子类,我们只使用一次。就可以使用匿名内部类。匿名内部类使用方法的本地变量也是要final修饰。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
| package com.czm.classes;
import javafx.scene.Parent;
interface Parents {
void print(boolean flag);
}
class Persion{
public void work() {
System.out.println("work……");
}
}
public class AnonymousInnerClass {
private int num1 = 1;
Parents father = new Parents() {
@Override
public void print(boolean flag) {
System.out.println("匿名内部类:"+flag);
System.out.println("外部字段"+num1);
}
};
Parents mothor = (e)->{
System.out.println("lamber实例化的匿名内部类:"+e);
};
Persion persion = new Persion(){
@Override
public void work() {
System.out.println("重写父类方法");
super.work();
}
};
void test1() {
int tt = 12;
Persion p = new Persion(){
@Override
public void work() {
System.out.println("在方法中使用后匿名内部类");
System.out.println(tt);
super.work();
}
};
p.work();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnonymousInnerClass anonymousInnerClass = new AnonymousInnerClass();
anonymousInnerClass.father.print(true);
anonymousInnerClass.mothor.print(true);
anonymousInnerClass.persion.work();
anonymousInnerClass.test1();
}
}
|
静态内部类
关键字static修饰,只能访问外部静态字段和方法,根成员内部类一样可以用public等修饰符修饰,不依赖于外部类,可直接外部类.内部类使用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
public class StaticInnerClass {
static int num = 2;
public static class StaticClass{
int num1 = num;
static {
System.out.println("初始化静态内部类");
}
public static void print() {
System.out.println("静态内部方法");
}
protected void test() {
System.out.println("test");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
StaticClass.print();
StaticClass staticClass = new StaticClass();
staticClass.test();
}
}
|
END








